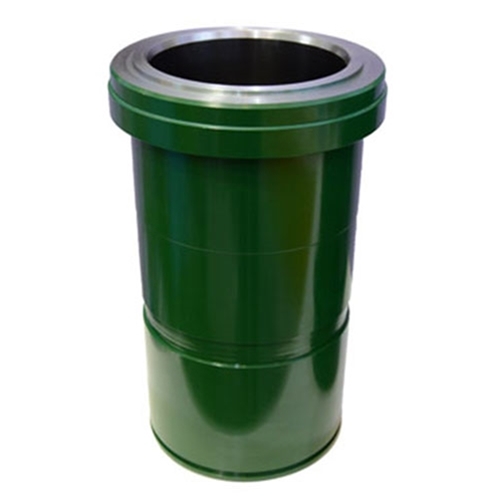
Ceramic cylinder liners typically have the following advantages:
1. Strong wear resistance: Compared to traditional bimetallic cylinder liners, its lifespan can be increased several times or even ten times, with a service life of up to 4000 hours or even 10000 hours;
2. Wear resistance and corrosion resistance: able to maintain good working condition under harsh working conditions, such as working in corrosive media, or operating in high-speed, high-pressure, and high-temperature environments;
3. High strength and hardness: capable of withstanding significant pressure and impact forces;
4. High precision: Low coefficient of thermal expansion, small size change during temperature changes, ensuring accuracy during use;
5. Good surface quality: Its ceramic lining has a uniform microstructure, and the surface has undergone multiple fine processing, resulting in good smoothness and glossiness;
6. Low overall cost: Although the price of ceramic cylinder liners themselves may be higher, the improvement and enhancement of their overall performance can significantly reduce maintenance, labor, storage, transportation, and other costs;
7. Environmental Protection: Ceramic materials do not rust, have obvious corrosion resistance, are pollution-free, and meet environmental protection requirements;
8. Reduce pump shutdown maintenance: can greatly reduce the complexity of underground situations and significantly lower the overall cost of drilling;
9. More resilient: For example, zirconia ceramic cylinder liners using phase change toughening technology have significantly improved strength, hardness, toughness, and thermal shock resistance;
10. Improving equipment operating efficiency: For example, the high thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramic cylinder liners can reduce heat loss.
However, ceramic cylinder liners may also have some limitations, such as certain requirements for installation conditions and supporting equipment, and may be easily damaged by impact in some cases. In specific applications, it is necessary to comprehensively consider its advantages and disadvantages based on actual working conditions and requirements.
{1}
{2}
{3}
{4}
{5}
{6}
{7}
{8}
{9}
{10}
{11}


 Service Hotline
Service Hotline