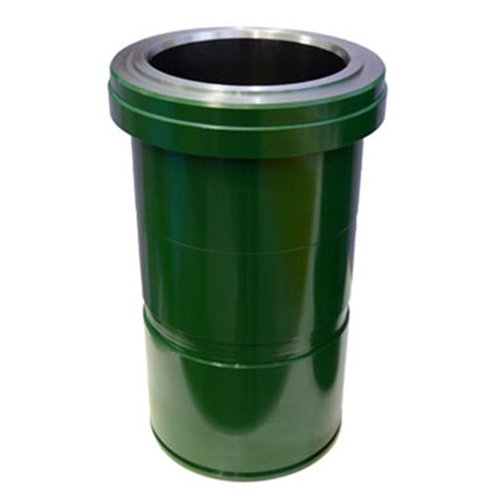
Bimetallic cylinder liner is an engine component mainly composed of two different metals. Usually, the inner layer is made of high-temperature resistant and wear-resistant alloy materials, such as chromium molybdenum alloy or nickel chromium alloy, which can maintain good mechanical properties and thermal stability at high temperatures, ensuring that the high temperature of the combustion chamber will not cause damage to it. The outer layer is made of corrosion-resistant and low-cost metals, such as cast iron or aluminum alloy, to provide protection and withstand mechanical impacts.
During the manufacturing process, these two metals are stacked together using precision casting or forging techniques to form a structure with strong adaptability to internal and external temperature differences. When the engine is working, the inner metal expands due to high temperature, while the outer metal expands less, which automatically adjusts the cylinder wall clearance, reduces wear, and improves cooling efficiency.
Overall, the bimetallic cylinder liner, with its material combination and design, achieves a balance between high temperature tolerance and economy, and is an important component in improving reliability and durability in modern engines.


 Service Hotline
Service Hotline