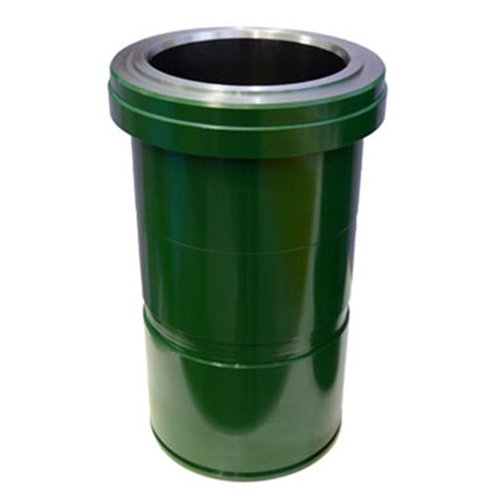
Bimetallic cylinder liner is a special engine cooling component, which is mainly composed of two layers of metal with different materials inside and outside. The inner layer is usually made of high-temperature resistant alloy materials, such as cast iron or aluminum, which are used to directly contact high-temperature gas and absorb heat; The outer layer is made of a metal with a lower coefficient of expansion, such as copper or stainless steel, and comes into contact with cooling water. When the inner layer expands due to heat, the outer layer remains relatively stable due to its small coefficient of expansion, forming a "thermal insulation layer".
The working principle is as follows: during the operation of the engine, the gas heats the inner metal layer, causing it to expand; Due to the constraints of the outer layer, the inner metal can only expand towards the outer layer, transferring heat to the outer layer and dissipating it through the cooling system to prevent the cylinder liner from overheating. After the engine cools down, the inner and outer metal layers shrink and return to their original state. This design effectively protects the cylinder liner, extends the engine life, and improves its thermal efficiency.


 Service Hotline
Service Hotline